Field: Biology
What ever happened to the first cryogenically frozen humans?
For decades, people have arranged to freeze their bodies after death, dreaming of resurrection by advanced future medicine.
Yale team partially revives dead pig organs an hour after death
Yale’s OrganEx technology has been used to partially revive the organs of dead pigs an hour after their hearts stopped beating.
Long COVID-19 and chronic conditions after viral infections may stem from an overactive immune response
Understanding the immunological mechanisms underlying long COVID-19 is the first step to addressing a quickly worsening public health problem.
The Singularity: When will we all become super-humans?
Are we really only a moment away from "The Singularity," a technological epoch that will usher in a new era in human evolution?
ADHD drugs might also treat Alzheimer’s disease
Scientists reviewed 40 years of clinical studies that assessed the effects of NA-targeting drugs, such as certain ADHD drugs, on Alzheimer’s.
Jeff Bezos is looking to defy death – this is what we know about the science of aging
Will Bezos’s company succeed in extending the human lifespan? Maybe. But we can all benefit from studying aging.
How natural “short sleepers” thrive on 4 hours of sleep per night
Natural "short sleepers" thrive on only four to six hours of sleep per night. Could their genetics explain why?
How will humans change in the next 10,000 years?
If humans don’t die out in a climate apocalypse or asteroid impact in the next 10,000 years, are we likely to evolve further?
MIT engineers 3D-print rubbery brain implants that don’t “stab” the brain
How do you engineer an implant that doesn't harm an organ as soft as tofu? MIT engineers 3D-printed new soft brain implants.
The sci-fi plan to create artificial gravity on the moon, Mars
To create artificial gravity for off-world explorers, Japan plans to build spinning, cone-shaped facilities on the moon and Mars.
New discoveries are rewriting the rulebook for regenerating limbs
Human limb regeneration is closer to reality thanks to new studies that refine our understanding of what mammals need to regrow body parts.
10-second balance test is a powerful predictor of death for older adults
Adults aged 51-75 who were unable to balance on one foot for ten seconds had an 84% higher risk of death than their peers who could.
A new delivery method for drugs that can’t withstand stomach acid
In order for a drug to get to the small intestine, it must first get past the highly acidic environment of the stomach.
Do optimists really live longer? Here’s what the research says
Research shows if you cultivate a more optimistic mindset, you might further increase your chances for a long life.
Wearable tech: eating and playing our way to a longer lifespan
Wearable devices can detect the specific molecules in food and our body’s response to it, allowing us to make better dietary decisions.
Gene editing gone wrong: Scientists accidentally create angry hamsters
A team of scientists used gene editing to create what they thought would be a calmer rodent. Instead, the gene-edited rodents were angrier.
This molecule may be the “secret sauce” of exercise — but it won’t work as a pill
Administering Lac-Phe to obese mice significantly lowered their appetite, reduced body fat, and improved glucose tolerance.
Engineers develop nanoparticles that cross the blood-brain barrier
Tested using a new brain tissue model, the particles may be able to deliver chemotherapy drugs to cancer patients.
The key to fighting fungal infections may have been inside us all along
MIT researchers have discovered that complex molecules in mucus can keep fungal infections in check.
“Stealth bomb” for cancer unlocks powerful immune attack
A "masked" cancer drug stealthily trains immune system to kill tumors while sparing healthy tissues, reducing treatment side effects.
Self-healing robot skin created out of human cells
University of Tokyo researchers have created a living skin, made from human cells and collagen, for a robotic finger.
Study reveals the dynamics of human milk production
MIT researchers performed a large-scale study of the cells in human breast milk, allowing them to track how these cells change over time.
Genetic mutations can be benign or cancerous – here’s a new way to identify them
Identifying the difference between normal genetic variation and disease-causing mutations is vital for determining a person's treatment.
Why haven’t plastic-eating bacteria fixed the plastic problem yet?
Texas scientists have created an enzyme that could keep billions of pounds of plastic out of landfills.
First CRISPR’d cockroaches open door to other gene-edited insects
It’s now easier for scientists to create gene-edited insects thanks to a new technique called “direct parental CRISPR.”
Ultrathin fuel cell uses the body’s own sugar to generate electricity
Batteries have a limit to how small they can be made, and they need to be charged. What if you could power your own medical device?
Gene editing could reverse anxiety and alcohol-use disorder
Gene editing may be a treatment for anxiety and alcoholism in adults who were exposed to binge-drinking in their adolescence.
‘Mad honey’: The rare hallucinogen from the mountains of Nepal
On the mountainsides of Nepal and Turkey, bees sometimes produce a strange and dangerous concoction: mad honey.
Joystick-operated robot could help surgeons treat stroke remotely
With a modified joystick, surgeons in one hospital may control a robotic arm at another location to safely operate on a patient.
How Robert Langer, a pioneer in delivering mRNA into the body, failed repeatedly but kept going
Langer published the first paper to show that it was possible to deliver nucleic acids like RNA and DNA to the body via tiny particles.
Inspired by kombucha tea, engineers create living materials
A symbiotic culture of specialized yeast and bacteria can generate tough materials able to perform a variety of functions.
We overwash our bodies because bad odors are uniquely disgusting
Overwashing is bad for skin health, but many people do it anyway. One reason is that our brains intimately associate stink with disgust.
Bacteria living inside tumors help cancer spread through the blood
Intracellular bacteria promote cancer metastasis by enhancing the tumor cells' resistance to mechanical stress in the bloodstream.
New $5-device allows healthy sperm cells to isolate themselves
About 10% of men are infertile, and often their sperm is to blame. This device could help separate the healthy cells from the others.
Build strength with only three seconds of weight lifting per day?
Researchers have found that a four-week program consisting of three seconds of weight lifting per day for five days a week boosts strength.
Researchers identified over 5,500 new viruses in the ocean
These discoveries help scientists better understand not only the evolutionary history of viruses but also the evolution of life on Earth.
MIT’s new bacteria protects guts from antibiotic-caused dysbiosis
An engineered bacteria protects the gut microbiome from antibiotics to help people battle infections without risking dysbiosis.
Should we use genome editing to make better babies?
Over the years, many different people, from preachers to philosophers, have voiced their concerns over the safety and ethics of gene editing.
Reversing hearing loss with regenerative therapy
MIT spinout Frequency Therapeutics’ drug candidate stimulates the growth of hair cells in the inner ear.
A physician didn’t shower for 5 years. Here’s what he found out.
Hygiene rituals are as old as recorded civilization, but capitalism has spurred us to use increasingly elaborate and expensive regimens.
Mammals dream about the world they are entering even before birth
A study finds that baby mammals dream about the world they are about to experience to prepare their senses.
Blasting mushrooms with UV light boosts vitamin D by 4,600%
Roughly half the world population, including in America, has insufficient levels of vitamin D. UV irradiated mushrooms can help.
Anti-aging isn’t a scam, but immortality almost certainly is
A new biotech firm with $3 billion in funding has announced plans to combat aging. But what does that mean for human life span, exactly?
How the antidepressant Prozac could treat blindness
Prozac is a widely used antidepressant. Data indicates that the drug could be used to prevent blindness due to macular degeneration.
Digital sound archives can bring extinct birds (briefly) back to life
Sound recordings remind us that these beings are invaluable, and that humans have a duty to preserve them.
Spinal cord implants help paralyzed people walk again
A new spinal cord implant uses electricity to reawaken spinal neurons.
New tech cuts years off of DNA sequencing
The Stanford Medicine team set a new record for DNA sequencing. They went from obtaining a blood sample to diagnosing an illness in just 8 hours.
Sonic waves could help bones grow back after cancer
A technique that turns stem cells into bone cells using only sound waves could help people regrow bone destroyed by disease.
Researchers convert donor lungs to universal blood type
A new study reveals that if donor organs were treated with specific enzymes, any organ could become "universal" and be more compatible with recipients of any blood type.
How mRNA and DNA vaccines could treat autoimmune disorders, genetic diseases, and more
Using DNA or an mRNA vaccine, researchers are investigating the feasibility of essentially replacing missing genes that cause disease.
Despite its disastrous effects, COVID-19 offers some gifts to medicine
While it’s still too early to draw conclusions, there's emerging evidence between autoimmune disorders and the virus that causes COVID-19.
Diamond-like starfish skeleton unlike any discovered in nature
The skeleton of the knobby starfish has a structure unlike any other found in nature so far, and it could inspire new lightweight ceramics.
Opioid overdose: A bioethicist explains why restricting supply may not be the right solution
Since the unpredictability of drug supply increases overdose risk, making the drug supply predictable should be part of the solution, right?
Take a look at the deepest known squid, just found
NOAA scientists used an ROV to spot a ghostly cephalopod, known as a bigfin squid
Horseshoe crabs are drained for their blue blood. That practice will soon be over.
One of humanity’s strangest and most macabre activities is slowly coming to an end, a trend that every horseshoe crab should celebrate.
Golden blood: The rarest blood type in the world
Golden blood, despite sounding like medical nonsense, is actually the nickname for Rh-null, the world’s rarest blood type.
First gene therapy for Tay-Sachs disease successfully given to two children
After 14 years in development, gene therapy has helped two children surpassed their life expectations and live seizure-free.
“BioDome” triggers near-complete limb regeneration in frogs
A new limb regeneration treatment allowed adult African clawed frogs to regrow near-complete functional legs following amputation.
Are stem cells about to cure baldness?
Researchers have reprogrammed stem cells to successfully grow human hair on animals, hinting at a potential cure for baldness.
Reasons to be optimistic in 2022
It can be tough to feel positive after the past two years. But a closer look at the recent past provides reasons for optimism in 2022 and beyond.
Top 4 biotech breakthroughs of 2021
New biotechnology breakthroughs took on viruses, parasites, and genetic diseases this year.
Microbots in your blood could help destroy cancer
Shape-shifting, magnetic microbots could become assassins for cancer — destroying tumors without the usual collateral damage on the rest of the body.
Dead bodies keep moving for more than a year after death, study finds
Australian scientists found that bodies kept moving for 17 months after being pronounced dead.
Blood and stool samples from 1980s link HIV to gut microbiome
A person’s chances of getting HIV appears to be influenced by the gut microbiome, suggesting it might help us prevent the disease.
Why do “young blood” transfusions help aging mice?
Young blood transfusions may combat signs of aging in older mice by increasing the production of a specific protein: Klotho.
10 surprising things we’ve learned about death
Modern science has demystified death by divulging its biological processes, but many questions remain.
Scientists got an animal to breathe without oxygen
Scientists discovered a way to keep tadpoles alive, even without environmental oxygen — by injecting photosynthetic algae into their brains.
Lizard regenerates perfect tail thanks to stem cells
A USC study that prompted lizards to regenerate tails that were “perfect” could help facilitate breakthroughs in human regeneration.
The bold plan to bring back the American chestnut
Researchers plant a small experimental orchard of hundreds of transgenic American chestnut trees near the coast of Maine, to restore the species.
Farmers in England begin massive DIY “rewilding” effort
Farmers in East Anglia are organizing what may be England’s largest rewilding project.
Series|
Challengers
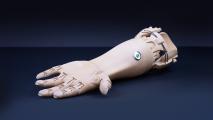
26-year-old builds $8,000 mind-controlled bionic arms
Bionic arms used to cost $80,000. Now, a young engineer has lowered the cost by over 90%.
DeepMind releases massive protein structure database
DeepMind is releasing a massive database of protein structure predictions that includes all the molecules in the human proteome.
The world’s first needle-free diabetes test
A needle-free diabetes test that measures glucose levels from saliva, not blood, could be ready for consumers as soon as 2023.
Castration linked to younger DNA and biological age
A study measuring biological age in castrated sheep has yielded a discovery that could inform anti-aging research for people.
Anyone can now make mouse-human chimeras
A newly published how-to guide for making mouse-human chimeras could lead to treatment breakthroughs for countless diseases.
Mouse embryos with beating hearts grown from stem cells
Mouse embryos with muscles, blood vessels, and beating hearts have been grown from stem cells — bringing lab-grown organs closer to reality.
3D-printed liver tissue may be first step to lab-grown organs
A NASA challenge designed to accelerate tissue engineering has announced two winning teams, both of which used 3D bioprinting to create human liver tissue.
Want strong teeth? Eat this candy.
Researchers claim to have invented an experimental breath mint that may renew tooth enamel and strengthen teeth, and it’s already headed into human trials.
Microscopic animals revived after 24,000 years in permafrost
A multicellular animal called the bdelloid rotifer has used cryptobiosis to survive in the Siberian permafrost for at least 24,000 years.
Editing one gene extends mouse life expectancy by 23%
By modifying just one gene, researchers were able to extend the life expectancy of mice by 23%, and they think their results may translate to humans.
The entire human genome has (finally) been sequenced
Researchers have finally sequenced the complete human genome, filling the gaps in the Human Genome Project’s historic first draft.
New lab-grown mini hearts have a human-like beat
Researchers created the first human mini heart in the lab. The mini hearts, called cardioids, have developed distinctly beating chambers, which fire in sync.
Birds, frogs, and reptiles use sound to “program” embryos
Sound appears to play a larger role in animal development than previously thought, affecting how a variety of species prepare for life outside the womb or egg.
"Defective" embryos can actually self-correct in the womb
PGT-A, a genetic test used to screen embryos for aneuploidy prior to in vitro fertilization, appears to be excluding many viable options.
Human lifespan may have a hard limit: 150 years
The human lifespan is limited to 150 years, according to a new longevity study focused on the body’s ability to bounce back from stressful events.
These bacteria grow biodegradable “Aquaplastic”
Scientists genetically modified E. coli to create a plastic called "aquaplastic," which can be transformed into a three-dimensional shape just by adding water.
Sperm may play a bigger role in pregnancy than we thought
Sperm appear to play a bigger role in pregnancy than previously believed, not only fertilizing the egg, but also “persuading” the female body to accept it.
Old dogs are helping scientists combat human aging
By studying donated tissues stored in a pet dog biobank, researchers have uncovered a genetic link between brain aging in canines and humans.
Supercentenarians’ DNA reveals clues to human longevity
A human longevity study involving people over the age of 105 has found that genetic variants linked to DNA repair appear to contribute to a longer life.
"Octopus vision" may help prevent human blindness
A new medical device that gives optometrists a fast, easy way to monitor a key macular degeneration risk factor was inspired by octopus vision.
New blood test could predict the onset of labor
Stanford University researchers have identified blood-based biomarkers that can be used to predict the onset of labor in pregnant women.
Customized stem cells could show us how dementia happens
By turning human cells into induced pluripotent stem cells, researchers hope to finally map the genetic path to Alzheimer’s disease.
Scientists may have figured out how to fight prion disease
Researchers believe they have found a spot on a mutated prion protein that can lead to brain-spongifying disease.
Bacteria nanomachines fire smart missiles that could replace antibiotics
Researchers want to use bacteria-made nanomachines called tailocins to help fight enemy bacteria strains in the human body.
Nobel prize-winning chemist helps invent synthetic mucus
Mucins, the long proteins in mucus, have an array of bacteria-fighting properties. These artificial mucins can act like the real thing.
The next generation of living machines: xenobots 2.0
Made from the stem cells of a frog, “Xenobots” are tiny living machines. And researchers have just debuted version 2.0.
Stunning “agar art” grows pictures with bacteria and fungi
Agar art lets scientists tap into their creative sides by growing microbes into beautiful bioart scenes in petri dishes.
Researchers have developed a “plant communication” device
Plants emit weak electric signals. Researchers have developed a device to read and send signals back — a type of “plant communication.”
Researchers have grown a mouse embryo in a bottle
Researchers have grown a mouse embryo outside the uterus for longer than ever before, opening up the door to learning more about how mammals grow.