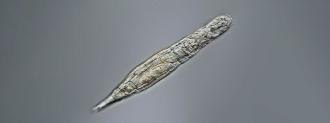
A microscopic, multicellular animal called the bdelloid rotifer has proven capable of surviving in the Siberian permafrost for at least 24,000 years. The discovery has given some hope that humans could one day be put into deep freeze and revived — but don’t count on it any time soon.
Cryptobiosis: To survive harsh environments, some creatures will put all their life-sustaining metabolic processes on hold and enter a state known as cryptobiosis.
While in this state, the organisms aren’t dead, but they’re not really living either — they don’t eat, reproduce, or even move. However, they can spring back to life if the environment becomes more hospitable in the future.
The discovery: At Russia’s Soil Cryology Laboratory, scientists collect samples of Siberian permafrost to see what creatures might be surviving within them in a state of cryptobiosis.
“We put a piece of permafrost into a petri dish filled with (a) suitable medium and wait until organisms that are alive recover from their dormancy, start moving, and multiply,” researcher Stas Malavin told Live Science.
This has led to the discovery of mosses, plants, and single-celled microbes capable of long-term cryptobiosis, but the scientists have now reported finding and reviving multicellular animals (the tiny rotifers), which were even able to reproduce after thawing.
What’s new: We already knew that rotifers could enter cryptobiosis, but previous studies had only shown that they could survive for 10 years on ice — the Siberian permafrost was 24,000 years old.
“Our report is the hardest proof as of today that multicellular animals could withstand tens of thousands of years in cryptobiosis, the state of almost completely arrested metabolism,” Malavin said in a press release.
Why it matters: Rotifers are more complex than the other organisms discovered biding their time in permafrost — they have brains, muscles, reproductive systems, and more.
Moving from a single-celled organism to one with a gut and brain is a big step forward.
Stas Malavin
The discovery that such complex creatures can survive in cryptobiosis for millennia pushes the limits of what researchers thought was possible, and by studying the organisms, we might find ways to better cryo-preserve human cells, tissues, and organs.
The rotifers might even inform research focused on freezing and reviving living humans so they could make decades- or century-long journeys through space without aging — but don’t expect people to be capable of cryptobiosis in the immediate future.
“(T)he more complex the organism, the trickier it is to preserve it alive frozen and, for mammals, it’s not currently possible,” Malavin said. “Yet, moving from a single-celled organism to an organism with a gut and brain, though microscopic, is a big step forward.”
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].