Naoki Yamanaka has an idea on how to stop mosquitoes, those plagues-on-wings: What if they just never grew up?
In a move akin to Peter Pan, the UC Riverside entomologist believes it may be possible to chemically arrest mosquitoes’ development — thus preventing them from maturing, mating, and reproducing — while leaving other insect species unaffected.
“It is impossible to make mosquitoes go extinct,” Yamanaka said. (Although maybe we should try!)
Naoki Yamanaka believes it may be possible to chemically arrest mosquitoes’ development while leaving other insect species unaffected.
And given that insecticides are prone to losing their potency, we need more tools to combat mosquitoes and their diseases.
“Depending on one tool to control them is dangerous. As the climate heats up, it creates even more favorable conditions for them to multiply, and they’re only likely to become a bigger problem, especially in Southern California.”
Bringing up buggy: Yamanaka’s idea hinges on an important steroid hormone called ecdysone — the “molting hormone.” This hormone is essential to growth and development; without it, insects simply won’t mature.
Scientists originally thought that ecdysone can just come and go through the cellular membrane willy-nilly, but Yamanaka’s research showed that it actually requires another special protein to shepherd it in and out of fruit fly cells.
According to UC Riverside, every insect known to science needs ecdysone at some step in the life cycle, and every insect Yamanaka has tested has had the same transporter proteins that he found in fruit flies.
But not all of the transporters.
Arrested development: In his new study, published in PNAS, Yamanaka used the mosquito Aedes aegypti — a human-leeching public health scourge that carries, among other things, yellow fever, dengue, and Zika — to discover that mosquitoes only have three of the four ecdysone transporters that fruit flies have.
“This primary one is somehow, mysteriously, missing in mosquitoes,” Yamanaka said.
All of those proteins are present in insects, but the three that the mosquito possesses “are dispensable for fly development and reproduction,” the researchers wrote.
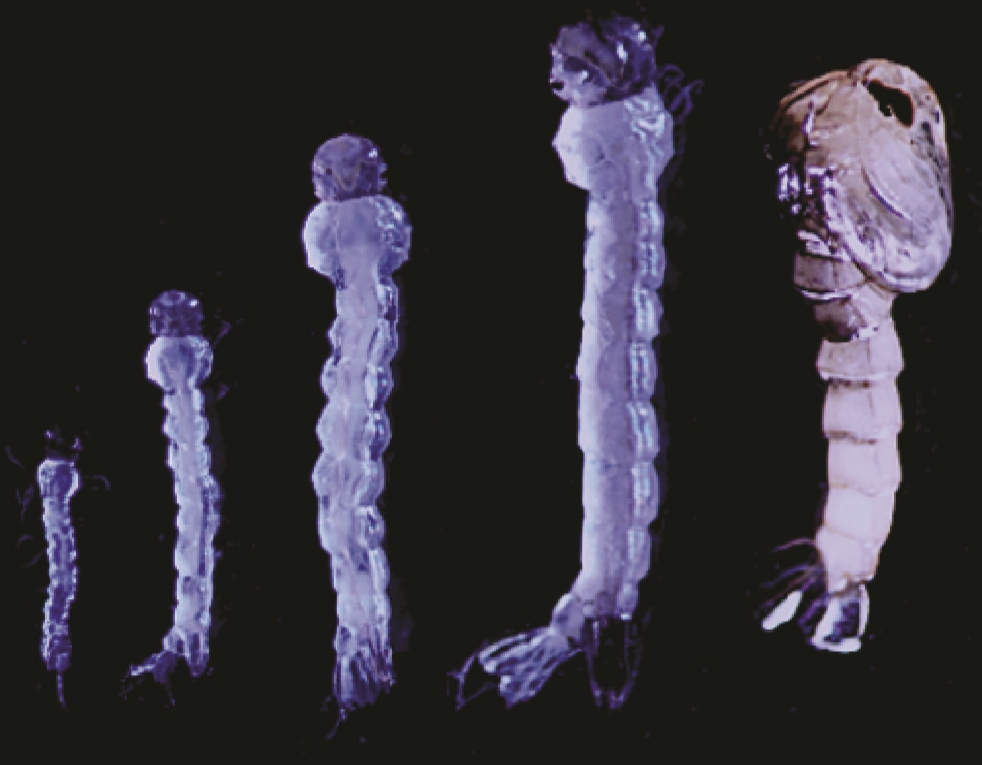
This means that targeting those three ecdysone transporter proteins — which seem unnecessary for other insects to mature — could potentially halt mosquitoes’ development in their tracks, while leaving other insects unaffected.
“We can develop chemicals to block the functions of these ecdysone transporters but do not affect the original transporter that is so key for other insects,” Yamanaka said.
Yamanaka’s lab is now looking for chemicals that can halt the mosquito’s ecdysone transporters and send the insects to Neverland — second star to the right and straight on til mourning.
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].






