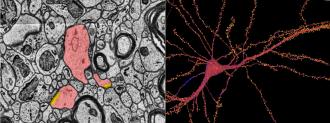
Researchers from Google and Harvard have released the most detailed map ever created of the human brain.
The map (called a connectome) contains “imaging data that covers roughly one cubic millimeter of brain tissue, and includes tens of thousands of reconstructed neurons, millions of neuron fragments, 130 million annotated synapses, 104 proofread cells, and many additional subcellular annotations and structures,” according to Google AI Blog.
Using a tool called the Neuroglancer (a cyberpunk novel if I’ve ever heard one!), you can browse that brain detail yourself.
What’s a connectome? A connectome is the product of brain mapping. The resolution of a connectome is so fine that we can see the brain on a cellular level — neurons, synapses, a nanometer-scale map. As one can imagine, this is a difficult task.
To work on their connectome of a mouse brain — the “mouseshot” — researchers at the University of Chicago and Argonne National Laboratory harnessed one of the world’s most powerful supercomputers.
There’s just too much data for human beings to sift through (assuming anyone working on it wants to live to see the result), and since we don’t yet have a mouse map, you can imagine how large a leap it would be to get a connectome of the entire human brain.
Google, working with the Janelia Research Campus, already laid claim to the largest connectome yet, putting out an intricate map of the mighty mind of the fruit fly last January. And we’ve got only one complete connectome thus far, of the brain of a roundworm, known as C. elegans.
A small piece of a big puzzle: To create the connectome, researchers from Google and Harvard’s Lichtman Lab began by taking a tiiiiiiiny sample of brain from the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex, Interesting Engineering reports.
After staining the sample and coating it, it was cut into over 5,000 slices just nanometers thick. Those slices were scanned by an electron microscope, with the end result being 225 million 2D images.
Those millions of images were compiled into a 3D image, which a machine learning algorithm then parsed, identifying the millions of different structures inside the connectome.
Here’s the fun part: the dataset, of this one cubic millimeter of one human brain, needs 1.4 petabytes of storage — about a million gigabytes.
It’s a neat illustration of the massive complexity of our most mysterious organ.
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].